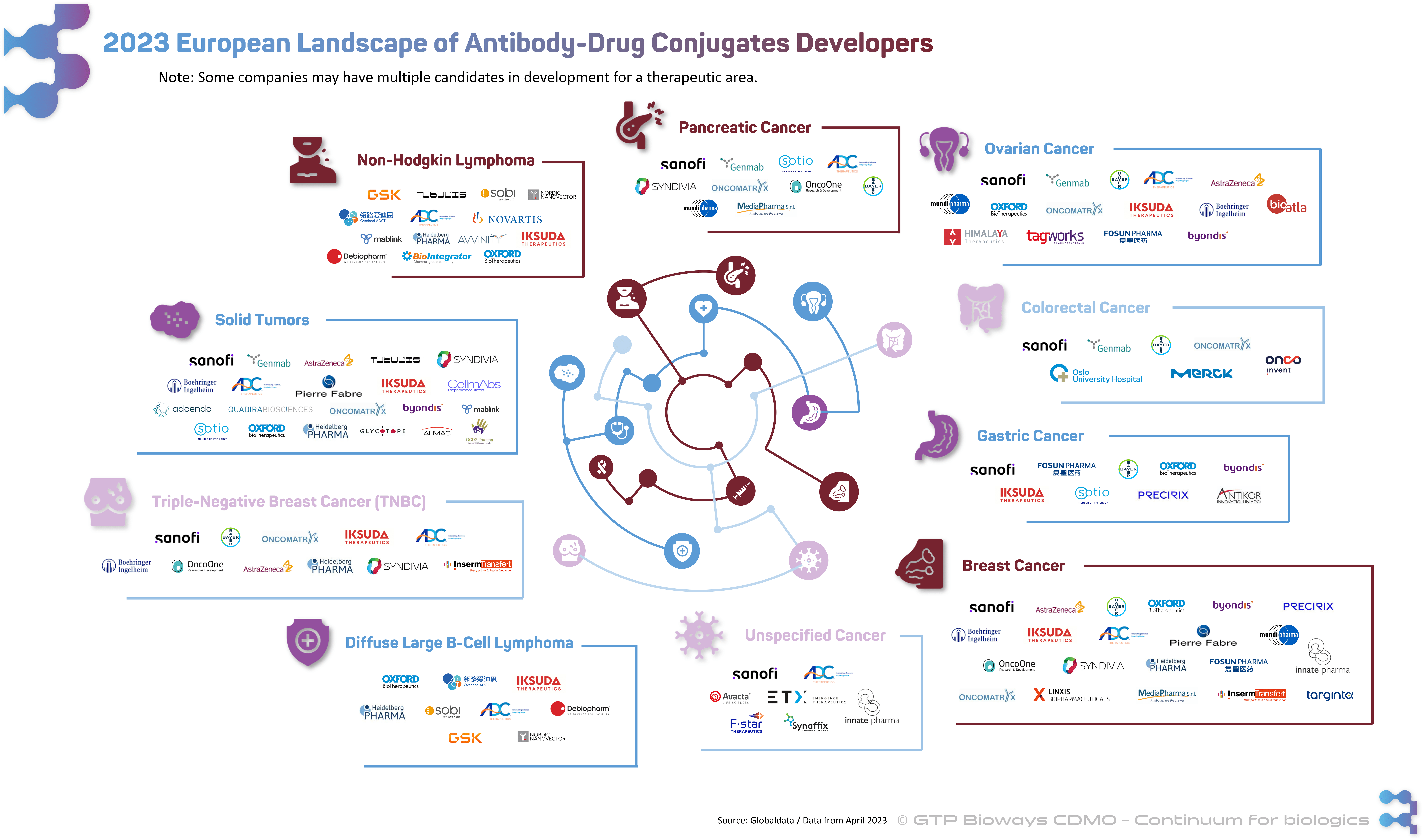
In the dynamic landscape of therapeutic development, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) have emerged as a ground-breaking class of biotherapeutics. ADCs are the result of a powerful fusion of monoclonal antibodies and potent cytotoxic drugs, enabling targeted delivery of highly effective treatments to specific cells or tissues.
The ABCs of Antibody Drug Conjugates
ADCs consist of three essential components: a monoclonal antibody, a linker, and a cytotoxic payload. The monoclonal antibody specifically targets antigens overexpressed on cancer cells, allowing precise delivery of the payload.
The successful development of ADCs hinges on a meticulous target selection. Identifying antigens that are highly expressed on cancer cells while sparing healthy tissues is crucial.
Challenges of Antibody-Drug Conjugates Process Development
Antibody Engineering: Monoclonal antibodies are extensively engineered and optimised to enhance their binding affinity, selectivity, and stability. Many techniques play a vital role in creating highly potent ADCs.
Linker Selection: The linker acts as the bridge between the antibody and the cytotoxic payload. Its role is multifaceted, facilitating stability, controlled release of the payload, and minimising off-target effects. The selection of an appropriate linker is a critical step in the development of ADCs.
Payload Design: The cytotoxic payload is the therapeutic component responsible for inducing cell death. A wide range of cytotoxic drugs, including chemotherapeutic agents, DNA-damaging agents, and microtubule inhibitors, are used based on their mechanism of action and potency
Clinical Applications of Antibody Drug Conjugates and Future Perspectives
Bioconjugates have shown remarkable promise in the treatment of various cancers, including breast cancer, lymphoma, and leukemia. Their targeted approach offers the potential for increased efficacy, reduced side effects, and improved patient outcomes.
Ongoing research aims to overcome current limitations and explore new avenues for ADC development. This includes exploring novel antibody formats, improving payload potency, and refining linker technologies to enhance ADC stability and therapeutic index.
Antibody-drug conjugates represent a transformative approach in the field of therapeutic development. By harnessing the power of monoclonal antibodies and cytotoxic payloads, antibody-drug conjugates offer a targeted and potent solution to combat cancer and other diseases. With continued advancements and refinements in the development process, ADCs hold immense promise in revolutionising patient care and improving treatment outcomes.